Physiotherapy – electrotherapy, ultrasound therapy, shockwave therapy
section-064d32a
Physical therapy is a branch of physiotherapy that uses natural or device-generated physical stimuli—such as electrical current, ultrasound, or acoustic waves—to support the treatment of pain, inflammation, and injuries. It is an excellent complement to manual therapy and exercise.
Below is a description of the three most commonly used methods: electrotherapy, ultrasound therapy, and shockwave therapy.
Electrotherapy
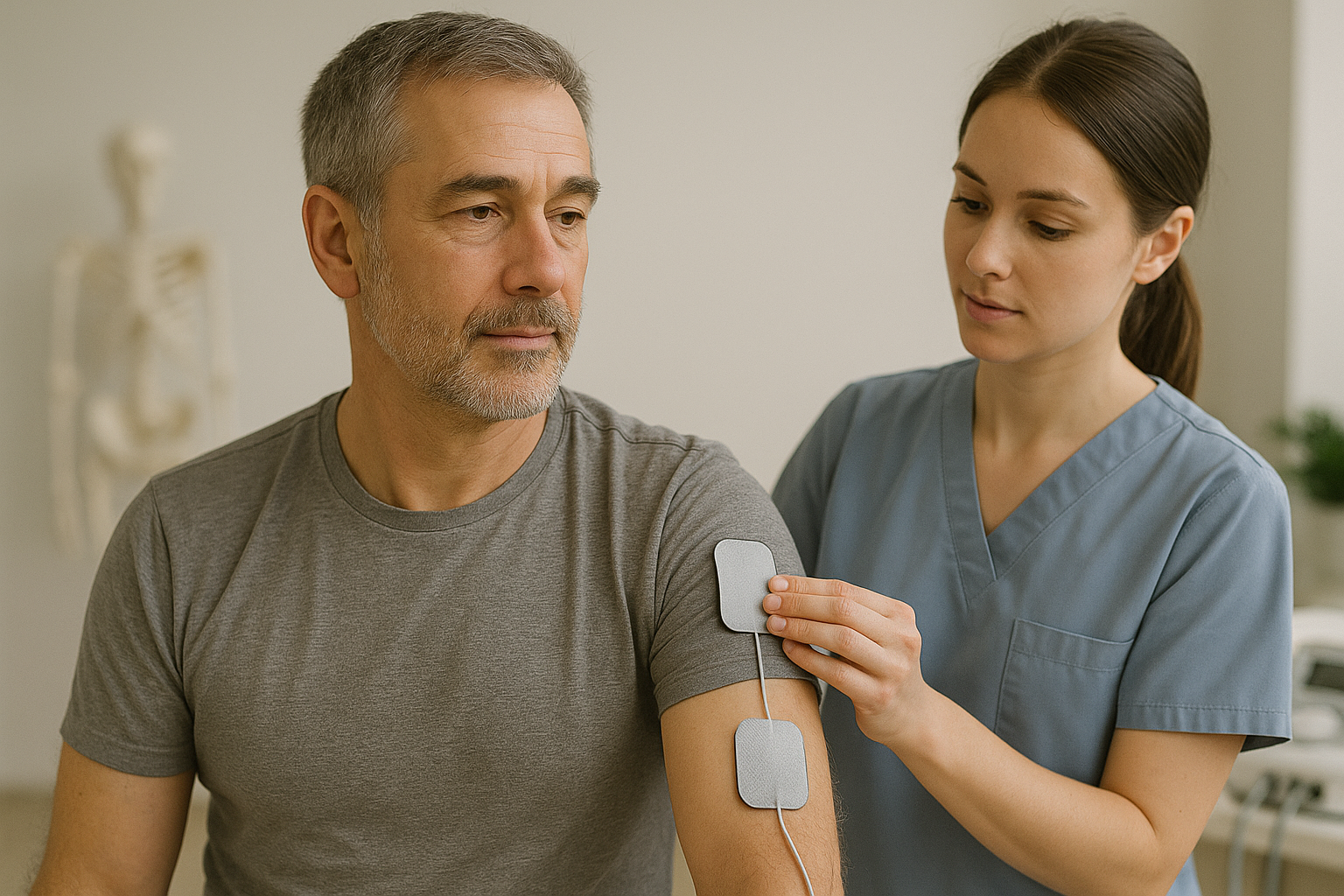
Electrotherapy involves the use of various types of electrical currents for therapeutic purposes.
Effects:
- reduces pain (analgesic effect)
- decreases muscle tension
- improves blood circulation and tissue nourishment
- accelerates healing
- can stimulate weakened muscles
Used for:
- spinal and joint pain
- muscle tension and overload
- neuralgia
- post-injury pain
- muscle weakness (e.g., after surgery)
Ultrasound therapy
Ultrasound therapy uses high-frequency sound waves that penetrate deep into the tissues.
Effects:
- reduces inflammation
- accelerates regeneration
- relaxes soft tissues
- improves microcirculation
- reduces pain
Used for:
- tendinopathies (e.g., Achilles tendon)
- muscle pain and overload injuries
- scars and adhesions
- enthesopathies
- joint disorders
Shockwave therapy (ESWT)
A modern and highly effective form of therapy that uses powerful acoustic wave impulses.
Effects:
- breaks down calcifications and adhesions
- strongly stimulates regenerative processes
- improves blood circulation
- reduces chronic pain
- accelerates tissue healing
Used for:
- heel spurs
- tennis and golfer’s elbow
- plantar fasciitis
- chronic tendon pain
- painful trigger points
- tendinopathies and calcifications